What we want to achieve is a DOS application (ftp, web browser) to communicate with an application or service on a remote computer. To do so, this application will need to be able to deliver data (bits) to the network interface card (or the serial port and then on to the modem) so that this device can send the bits to the remote computer, where -hopefully- they will be understood.
We'll only discuss how to successfully send those bits to the other machine. Whether or not that machine, or the software running on that machine, will respond, and whether or not that response will be what you like it to be, is beyond the scope of this article. You can successfully send an HTTP request to a web server, but if the web page you request does not exist, ... You can successfully send a username and password to a server, but if you're not a legitimate user ... You can successfully send a request to get a cup of coffee from an ftp server, but ...
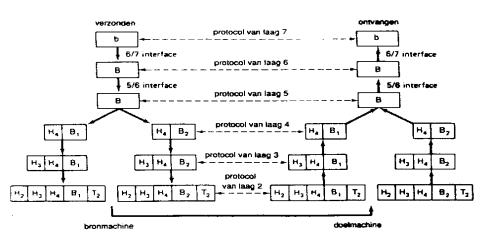
In the example of the web browser : your web browser will create HTTP packets that need to be sent to the web browser. Your network card doesn't know anything about HTTP packets. Therefore, through a number of steps, each HTTP packet will be modified : bits will be added, the packet may be split into 2 ore more packets, more bits may be added, etc. until they have a format your network card can handle. (For a little more detailed explanations, see First Steps in Networking).

This assembling and disassembling of packets is done by software, often called 'driver', 'layer' or 'interface'. Sometimes a program can cover more than one step, so you will not necessary always see the 7 levels mentioned in the OSI reference model. The TCP/IP model, on the other hand, only describes what happens from a 'network'-level and up. It does not explain how a modem or a serial port can get an IP address : the TCP/IP model looks simple because it skips the hard part : how does a computer connect to and identifies itself on the network.
This part, the host-to-network connection, is covered by other protocols and interfaces, such as PPP (modem dial up to the internet - protocol, solves the problem of how a serial port can get an IP address), or packet drivers (interface between IP-layer and network card device driver).
Our problem has now boiled down to : how do we give a DOS computer a 'host-to-network- connection that's capable of carrying IP packets. Although in theory there are many ways to do this (infrared light ? microwaves ? radio ? carrier pigeons ?), we'll limit ourselves to 2 common situations ; with a network card, or with a modem.
As we get closer to the actual implementation of the datalink level, the physical connection and the hardware, this explanation may tend to become more and more specific. A 3Com Etherlink III network adapter may require other drivers and configuration settings than another network card. It may come with configuration tools that are not available for other cards. Two PPP dialup programs may use different solutions for the same problem, and the software that needs to interact with the dialer will have to be adapted to that solution.
This is fairly simple. You put a network adaptor in your PC. If its an 'Ethernet' card, it will provide 'Ethernet' connectivity to your PC. You then need some software that can translate bits/bytes/packets in to ethernet frames on one hand, and translate ethernet frames to IP packets or or other packets (Novell Netware ? Windows file sharing ?) on the other hand. This software is called a 'driver'.
There are 3 standard interfaces for network drivers under DOS/Windows : NDIS, ODI and PKTDRV. If an Ethernet card has an e.g. an ODI driver, any protocol stack that wishes to interface with the network card can communicate to the ODI driver. This way, software developers don't need to develop a separate program for each make and model of Ethernet card. Likewise for Ethernet cards with NDIS Drivers and Packet Drivers.
NDIS is the foundation of most networking products from Microsoft. NDIS version 2 is real-mode/MS-DOS based NDIS. NDIS3 is protected mode/32-bit NDIS which was introduced in Windows for Workgroups.
ODI is the interface for most networking products from Novell. Pegasus Mail (for DOS) and Arachne also expect an ODI interface when they are used on a LAN.
PKTDRV was introduced by FTP software for their DOS TCP/IP applications such as PC/TCP. Freeware packet drivers for a wide range of ethernet cards can be found at Crynwr. A lot of TCP/IP applications for DOS expect a packet driver. Almost all Crynwr packet drivers are open source software. The manufacturer of your network interface card may also distribute packet drivers (and NDIS, ODI) on their web site.
Sometimes it is necessary to convert from one type of interface to another, e.g. if there is no packet driver for your ethernet card, while the application you use expects one. Software to do this is called a SHIM. A shim is a TSR or driver which converts from one interface to another. Examples are ODIPKT which provides a Pktdrvr standard interface on top of an ODI driver, and DISPKT9 which provides a Pktdrvr interface on top of an NDIS driver. Other software allows multiple applications or tcp/ip stacks to simultaneously interface with the (driver for the) network card.
These interfaces can be implemented in several ways. For DOS, they are often implemented as TSR programs (terminate and stay resident : programs that remain in memory so that they can be called upon), or drivers that have to be loaded in the config.sys. TSR's are usualy included in the autoexec.bat, so that they are loaded at startup, but they can also be run from an other bat file or from the command prompt. This allows you to keep them out of the memory until you need them (memory is scarce on old PC's).
Under Windows, drivers can also be loaded from the config.sys, or from .ini files (system.ini or application-specific ini file. Interfaces under Windows can be implemented as under DOS, or as dll or VxD (32bit Windows).
Commercial networking software will usually come with instructions and a setup utility that copies all necessary files to the correct location, creates configuration files, modifies autoexec.bat and config.sys to make sure all driers are loaded and other software is run when needed.In the Windows / DOS for Workgroups setup, you can find those drivers in the system.ini.file.
[386Enh] ... network=*vnetbios,*vwc,vnetsup.386,vredir.386,vserver.386 device=ifsmgr.386 netmisc=ndis.386,ndis2sup.386 netcard=elnk3.386 transport=nwlink.386,nwnblink.386,netbeui.386 [Network] multinet=nonet FileSharing=Yes PrintSharing=Yes LogonDisconnected=yes EnableSharing=Yes UserName=-removed- Workgroup=-removed- ComputerName=-removed- logonvalidated=no [network drivers] netcard=elnk3.dos transport=ndishlp.sys,*netbeui devdir=C:\WINDOWS3 LoadRMDrivers=No
The [network drivers] section shows elnk3.dos (NDIS 2 driver (DOS) for my 3COM Ethernet card). Additional software is made available in the [386 Enh] section. Here you'll find additional software drivers and settings for Windows' 386 Enhanced mode, e.g. NDIS3 driver and elnk3.386,the Windows3.11 driver for my 3COM Ethernet card.
But that's only for Windows. we were looking at DOS. Besides, free open source software is more appropriate if you want to try this at home.
Assuming a PC with MS-DOS v.6, with a 3COM EtherLink III 3c509B ethernet card.
First of all we need a Packet Driver for this card. It's called 3C5x9PD.COM, so it's executable and can be run from the command prompt or a batch file.
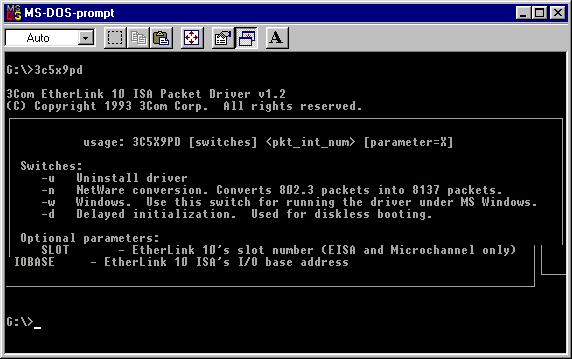
Apparently, we need to supply an interrupt vector, <pkt_int_num>, a software interrupt that other applications can use to find the location of the driver in the computer's memory, and use it to get their bits and bytes through the network adaptor on to the network. . These packet drivers usually get interrupt vectors 0x60,0x61,0x62, etc.
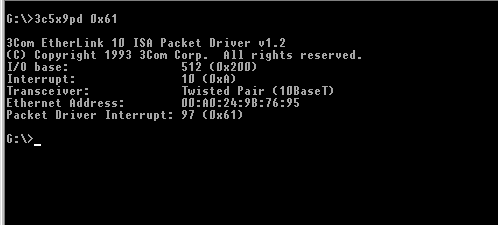
Note that the card itself has interrupt 10. This is the hardware interrupt of the network adapter, used by the network card to 'get the attention' of the CPU. It can (sometimes / usually) be modified either by jumper settings on the card itself, either with a configuration tool if that came with your NIC, either it's Plug and Play - but no P&P under DOS !
More hardware stuff : I/O base address (can be changed with the option 'parameter' as shown on the screen - in case it conflicts with other devices). This is the I/O address where the CPU can communicate with the NIC. Ethernet Address : Unique address, 'build into' the circuits of the network interface card. (a.k.a. MAC address). used to identify the device, and the computer where it is located, within the ethernet network. If you're on a network with Dynamic Host Configuration (dynamic IP addresses !), The DHCP server will associate an IP address to this MAC address.
As there is no general standard for DOS TCP/IP, DOS applications include their own TCP/IP stack. Next step is thus to setup your DOS TCP applications (mail ? browser, ...) and enter your network data in their configuration files, dialog boxes etc. These applications will know how to communicate with the packet driver, either by looking for it in the memory until they find it. It is also possible that you need to enter this location (0x60) in the configuration of your software.
For the sake of argument, well now install Trumpet DOS TCP/IP stack. It is conceived as a more general TCP/IP stack that several programs could use. (like Winsock does for Windows). It comes with some applications like finger, ping and FTP, and as it is a standard interface, it should be possible to write other applications for it as well - so if you're not yet a programmer, you might find some Trumpet-compatible TCP/IP applications on the web.
As we are talking about LAN, Local Area Network, it is assumed that you have, or will, set up a local network (e.g. 2 old PC's with network cards and a cross-link cable, or straight cable and a hub, etc ...). You have now become (by default) the network administrator, so you decide which pc gets what IP address, what your subnetmask will be, etc. Just make sure it makes sense. There's an excellent TCP/IP Primer in the network section of this web site - look for Daryll's TCP/IP primer - addressing and subnetting on the near side of the web. Note that the addresses etc. given in the following example are realistic for a home network.
The executable for Trumpet's DOS TCP/IP stack is tcpdrv.exe. You can supply all your network parameters (ip address, netmask, ...) as command line options. (there's a link to the readme file further down). You can also make environment variables to hold these values, and tcpdrv will read them and use them.
tcpdrv.exe will also look for a packet driver, and if you have installed one, it will find it and use it.
So a very simple way to provide TCP/IP connectivity to a DOS pc would be to collect all the software mentioned, put these files in a directory, and create a batch file to
here's a sample batch file
@echo off cls ECHO connecting over TCP/IP REM load packet driver at interrupt vector 0x60 3c5x9pd 0x60 REM set network information in environment variables as parameters for trumpet set IP=10.0.0.3 set GATEWAY=10.0.0.1 set NETMASK=255.255.255.0 set DOMAIN= set DNS=212.35.2.1 load Trumpet TCP/IP stack tcpdrv ECHO testing network with ping ping 10.0.0.3 ECHO if ping was successful, you're on
This batch file can now be seen both as a command to get your PC on the LAN over TCP, and as a configuration file (edit the batch file to change network parameters). When it's run, you clearly see how the packet driver is loaded, then how TCP is installed taking the network parameters you've entered.
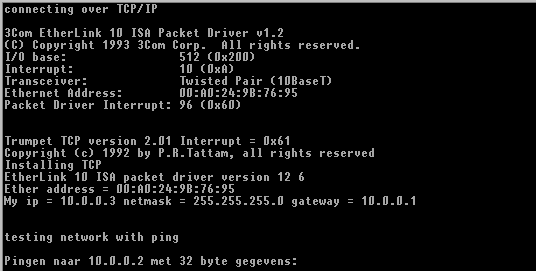
This seems to work - piece of cake. But I haven't tested this - the other PC, the one I should connect to, is temporary out of order due to a hard disk crash, ... But it looks as if it might work, doesn't it ?
Although this is supposedly more complicated than connecting to a LAN, there's far more documentation to be found on the web, so in a way it's even easier.
It is done in 4 simple steps :
The first step is easy : just plug it in. The characteristics ('properties') of the serial port taken all together make it a COM port ( a communication port). E.g. If your modem is on COM2, and your BIOS says that COM2 uses interrupt 4 and I/O address 2F8, then all communications software know where to find the modem, and use it to communicate with a remote system. This does mean that you'll have let this software know at what port your modem is, or which interrupt and I/O address it uses. This, and other modem commands (such as : which number to dial) can be put in a modem script or dialer script.
For step 2, 3 and 4, you may come across several different solutions :
Step 2 and 3 are usually combined in 1 program (a PPP-dialer). They usually can be used interactive : you type some modem commands (the 'modem string' and a command to make the modem dial a telephone number) and other input on the keyboard, they show the reply of the remote system on the screen. Or you can let them read the commands, the telephone number, username, password ... from a text file (script).
Instead of PPP (Point to Point Protocol), there's also SLIP, which is older and less advanced, but uses far less memory (which matters when you're using a really old machine. You'll need to find a provider that still supports SLIP, PPP is the standard these days.
TCP/IP software is often designed to work with PPP connections. In some cases, you may need to load an additional piece of software to enable the communication between the TCP/IP level and the PPP level. Or the dialer will arrange that for you and take care if this 4th step as well. Some TCP/IP programs will even take care of everything from the dialing up to and including the IP layer - or at least pretend they do so by loading the software for step 2, 3 and 4 themselves. You may even come across applications that cover everything, like a web browser for DOS that covers the whole range from dialing to showing web pages, in complete disregard of the layered approach of OSI and TCP/IP reference model. The layered approach, however, allows you to use the same connection configuration for whatever application you want to run : mail programs, web browsers, file transfer ...
These programs (often called 'packet drivers') will allow IP packets to run over your telephone line if a PPP connection has been established, establishing the necessary 'host to network' connection for TCP/IP. The TCP/IP applications, however, will need some 'network information' such as the IP address of your provider, the IP address of your PC, the subnet mask, (and maybe some more addresses e.g. a DNS server etc). If this information is static (always the same), it can be provided in configuration files (text files that software can read from, like the .ini files under Windows).
Often your Internet Service Provider will assign you an IP address dynamically (every time you connect, you get whatever IP address the ISP has available at that time. It is supplied while the PPP connection is established. You then need a way to inform the TCP applications of this address. People using TCP/IP under DOS have developed several ways to handle that, by saving this info in 'environment variables', exporting them into text files, etc. Study some examples such as Arachne (WWW Browser for DOS), Barebones E-mail for DOS, etc.
The first three are freeware/shareware, the 4th one is a commercial product from the 80's so it might be hard to find.
The following example uses dospppd for the ppp layer, and miniterm as dialer. miniterm is the dialer used by Arachne (copyright Arachne Labs). Miniterm uses arachne.cfg as configuration file.To dial a modem, the file may look like this :
[dialer] Dialer @MINITERM.EXE>PPP.LOG UseTerminal Yes Port 1 Irq 4 Base 0x3f8 Mode 8N1 Speed 115200 InitString AT&F1 DialString ATDT PhoneNumber 034004321 Autologin No PPPusername johnyBgoode PPPpassword 123456
The dospppd distribution contains 2 types of packet drivers : pppd.exe and epppd.exe. The difference is that epppd emulates an ethernet card; this means that after the connection is set up, it 'behaves' as an ethernet network adapter. This is to allow software that expects an connection over ethernet to communicate with the packet driver as if it were an (ethernet) network card. Both pppd and epppd can be used with command line options, or with a configuration file that contains the information the packet driver needs. Like this :
com1 115200 modem asyncmap 0 user johnyBgoode passwd 123456
Password an username are repeated because the remote computer (my internet provider) will want to check them at this stage (i.e. during PPP negotiations, not during the dial-up / login. These are two different authentication protocols (PAP : Password Authentication Protocol : you are asked to log in with username and password -- CHAP : Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol). Dospppd can handle both.
Next, all it takes is to run these 2 commands (e.g. in a bat file).
cls @echo off REM Connecting to Yoohoo ... miniterm pppdd file ppp.cfg
This is what it looks like on screen
dialing
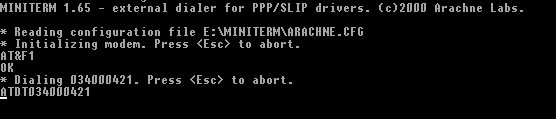
connecting
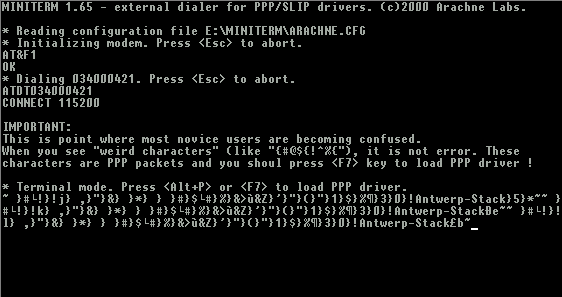
starting ppp
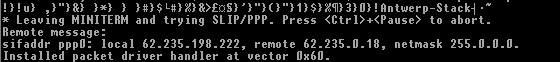
If the connection is made, pppd will collect IP (network) information from the remote computer (also visible on this screenshot) and create a batch file, IP-UP.BAT, that 'sets' this information in environment variables.
set myip=63.235.200.47 set remip=63.235.0.18 set netmask=255.0.0.0 set peermru=1500
You have now established a 'host-to-network' connection capable of running IP, For applications to use this connection, they need a TCP/IP stack : software that implements TCP/IP protocols. With DOS internet and other TCP/IP programs, this TCP/IP stack is usually integrated in the program. You do need, however, to inform the application that you're going to use, of the IP configuration.
About 50% of all DOS internet applications and TCP/IP software read their network information from a configuration file called wattcp.cfg. DOS provides > and >> to 'direct' output of a command or program to a file, so this can be used to write the values set in IP-UP.BAT to a text file such as wattcp.cfg. E.g. echo myip=%myip% >> wattcp.cfg will add the line myip=63.235.200.47 to the wattcp.cfg file.
> creates a new file, deleting any previous file with the same name. >> adds a line to an existing file or creates one of none exist. %____% indicates an environment variable. If this sounds like Chinese (while you are not), you may have to look up DOS in the Operating Systems section for more on DOS commands and batch files.
We add this to our batch file to automate the process, and add some cleanup (remove files from previous sessions so they won't interfere with the new session).cls @echo off REM remove files from previous session if exist wattcp.cfg del wattcp.cfg > NUL if exist ip-up.bat del ip-up.bat > NUL ECHO Connecting to Yoohoo ... miniterm pppdd file ppp.cfg REM call ip-up.bat to set IP info as environment variable call ip-up.bat REM write IP info from environment variables to wattcp.cfg ECHO myip=%myip% > wattcp.cfg ECHO remip=%remip% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO remip=%remip% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO netmask=%netmask% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO peermru=%peermru% >> wattcp.cfg
If you have an application that uses a different configuration file in stead of wattcp.cfg, you can of course redirect the output to that file. If your application uses environment variables but with different names (e.g. my_ip i.s.o. myip), you can create this variable and assign it its value with a statement like set my_ip=%myip%. You might want to use this technique to set environment variables for the Trumpet TCP/IP discussed earlier.
Your application might need information that is not provided by the ip-up variables : the address of a DNS server for instance. So you can either
you can -- according to which of the above methods you choose/need, add a matching statement to the batch file that you use to establish your connection. And you're ready to get on the internet with a DOS computer.
You may have noticed that this is a rather general (or vague) how to. You'll still need to figure out and decide a few things yourself. The main idea was to demonstrate how the physical and datalink layer are implemented (on a DOS computer), and then provide an "interface" to TCP/IP applications.
You do need some basic DOS knowledge to understand all this, (or learn very fast from the context.)
As shown in the DOS Internet setup, it is possible for DOS applications and batch files to read from and write to files, or create variables that other programs can use. If we now make several files, to mach multiple accounts with internet service providers, and we can specify to the connect.bat file which one to use, we can easily maintain several accounts.
Assuming we use two internet providers : Yoohoo and Africa Online (afro).
You can pass 'command line options' to the batch file that establishes your connection (connect.bat). In the batch file, they will be referred to by numbers : %1 is the 1st option, %2 is the 2nd option. So running connect.bat with connect yoohoo will have as effect that every time you mention "%1" in the batch file, it will be replaced with "yoohoo".
As we need a set of configuration files (for the dialer, for the dosppd, for additional network information, ...) for each provider, we could create these files and give the a name that refers to either yoohoo or afro, and have them copied / renamed at connect time..
| program/step | configuration file | yoohoo version | Africa Online version |
|---|---|---|---|
| dialer : miniterm | arachne.cfg | yoohoo.dlr | afro.dlr |
| ppp | ppp.cfg | yoohoo.ppp | afro.ppp |
| dynamic IP info | ip-up.bat | idem, is created by dospppd at connect time | idem, is created by dospppd at connect time |
| static IP info | my_ip.bat or myip.txt (depends on how you chose to do it) | yoohoo.bat or yoohoo.txt | afro.bat or afro.txt |
To connect to Africa Online, we copy the afro files and rename them to the corresponding configuration file. Likewise for Yoohoo. We inform the connect batch file by adding either afro or yoohoo at the comand line. In this batch file, we use %1 as variable to hold the command line option (yoohoo or afor).
cls @echo off REM remove any files left over from previous session if exist wattcp.cfg del wattcp.cfg > NULL if exist ip-up.bat del ip-up.bat > NULL if exist arachne.cfg del arachne.cfg > NULL if exist ppp.cfg del ppp.cfg > NULL REM copy matching file and rename to appropriate file name. copy %1.dlr arachne.cfg copy %1.ppp ppp.cfg copy %1.bat my_ip.bat copy %1.txt myip.txt ECHO Connecting to %1 ... miniterm pppdd file ppp.cfg REM call ip-up.bat to set IP info as environment variable call ip-up.bat REM write IP info from environment variables to wattcp.cfg ECHO myip=%myip% > wattcp.cfg ECHO remip=%remip% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO remip=%remip% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO netmask=%netmask% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO peermru=%peermru% >> wattcp.cfg REM supply additional network info from text file to wattcp type %1.txt >> wattcp.cfg REM run batch file to create additional environment variables isp.bat
If you can do 2 ISP accounts, you can do 3, 4, ... using the method described above. But it may be a bit messy to have all those files ... The following approach uses 1 text file per internet account. As an additional bonus, it does not put username and password in the text files, as this is considered unsafe.
Still assuming the same 2 accounts,
and a batch file called 'connect.bat' to get you connected to your internet provider, you could enter the following command at the command prompt :
connect yoohoo johnyBgoode 123456or, if you want to connect to Africa Online
connect afro JBGoode johnny
In the batch file, these options will be represented by numbers in the order that they were given at the prompt, so in the Africa Online case, "%1" becomes "afor", "%2" becomes "JBGoode", "%3" becomes "johnny".
We create 1 batch file per provider. Some local settings (e.g. modem configuration) may be put a separate file (localset.cfg), or included in the provider-specific batch file. These files wil be used by connect.bat to connect to the desired ISP.
The localset.cfg file may look like this :
;some changes in this file (e.g. com port, IRQ, ...) may need ; to be repeated in every isp-specific .bat file !! [dialer] Dialer @MINITERM.EXE>PPP.LOG UseTerminal Yes Port 1 Irq 4 Base 0x3f8 Mode 8N1 Speed 115200 InitString AT&F1 DialString ATDT
The Africa Online file (afro.bat) may look like this :
REM add Africa Online settings to arachne.cfg ECHO PhoneNumber 034004321 >> arachne.cfg ECHO Autologin No >> arachne.cfg ECHO PPPusername JBGoode >> arachne.cfg ECHO PPPpassword johnny >> arachne.cfg REM add Africa Online settings to ppp configuration file (ppp.cfg) ECHO com1 >> ppp.cfg ECHO 115200 >> ppp.cfg ECHO modem >> ppp.cfg ECHO asyncmap 0 >> ppp.cfg REM write Africa Online network info to wattcp.cfg ECHO dns >> wattcp.cfg ECHO [etc ...] ECHO create environment variables with additional TCP/IP info set ip=%myip% set nameserver=212.35.2.1 set nameserv=%nameserver% set dns=%nameserver% set ftpuser=anonymous set ftppasswd=jbg@africaonline.net etc. REM ******************************************** REM you can copy this file with a new name, REM and replace the values REM to create new ISP configuration REM *********************************************
connect.bat will be run with
connect afro JBGoode johnny
this is the modified connect.bat file :
cls @echo off REM remove any files left over from previous session if exist wattcp.cfg del wattcp.cfg > NULL if exist ip-up.bat del ip-up.bat > NULL if exist arachne.cfg del arachne.cfg > NULL if exist ppp.cfg del ppp.cfg > NULL REM *** multiple configuration setup *** REM write local settings to arachne.cfg type localset.cfg >> arachne.cfg REM run provider specific batch file to add data to arachne.cfg REM and create correct ppp configuration file call %1.bat REM add user name and password to arachne.cfg and ppp.cfg ECHO PPPusername %2 >> arachne.cfg ECHO PPPpassword %3 >> arachne.cfg ECHO user %2 >> ppp.cfg ECHO pwd %3 >> ppp.cfg REM *** multiple configuration setup ends *** ECHO Connecting to %1 as user %2... miniterm pppdd file ppp.cfg REM call ip-up.bat to set IP info as environment variable call ip-up.bat REM write IP info from environment variables to wattcp.cfg ECHO myip=%myip% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO remip=%remip% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO remip=%remip% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO netmask=%netmask% >> wattcp.cfg ECHO peermru=%peermru% >> wattcp.cfg REM additional network info is ISP specific, and therefore REM moved to provider specific batch file
That should do the trick. Keep in mind that you do not need to run afro.bat or yoohoo.bat yourself. Instead, run 'connect afro ... ... ' or 'connect yoohoo ... ..., ' ; and the connect.bat will run all files in the correct order.
Enjoy ...
In the late 1990's, I was playin with DOS and networking, mainly to get a feel for networking, DOS batch 'programming', and system administration, i.e. how you get programs and config files just right to do what it is you want them to do. This page is one of the write-ups from that period. Turns out it's the most linked-to page I have (according to Google Webmaster Tools). I had no idea TCP/IP on DOS was still such a hot topic.
I'm not updating this page anymore, but I'm leaving it here for anyone interested in the subject
Koen Noens, May 2012